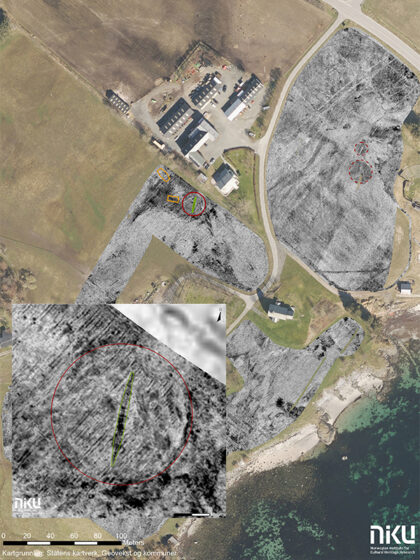
New geo-radar technology has uncovered traces of Karl XII's spectacular overland transport of galleys in 1718. The discovery provides new insight into one of Sweden's most fascinating military operations.

Digital archaeology
NIKU is adopting a broad range of new technology for the surveying, recording, and monitoring of cultural heritage sites.
See examples of our digital projects
NIKU's Department of Digital Archaeology works with various digital methods aimed at research and documentation of cultural heritage from both older and newer historic periods. See and explore the department's diverse work here.
Geophysical surveys
By using geophysical methods of investigation, we can investigate archaeological sites without resorting to physical intervention.
Registration of cultural heritage with drones
NIKU is certified as a drone operator and offers registration, terrain modeling, monitoring, and documentation of cultural heritage using drones.
Laser scanning
Laser scanning can be an important addition to documenting cultural heritage, and has proven to be an accurate and cost-effective method of documenting and monitoring different types of cultural heritage.
Image – based modeling
NIKU undertakes most types of dissemination and documentation projects. In our work, we combine the best of photogrammetry, laser scanning, and traditional documentation of cultural heritage

Projects
Here are some of our projects
Latest news
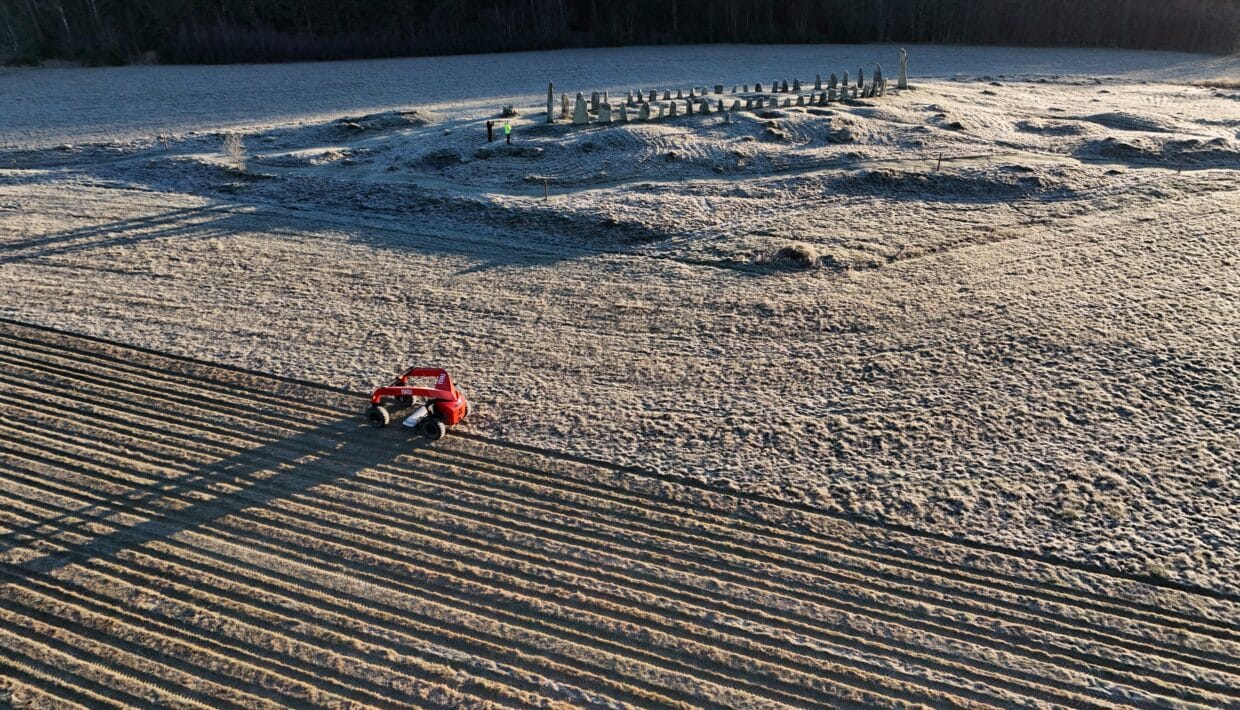

Historic discovery: Karl XII’s hidden transport route uncovered at Blomsholm
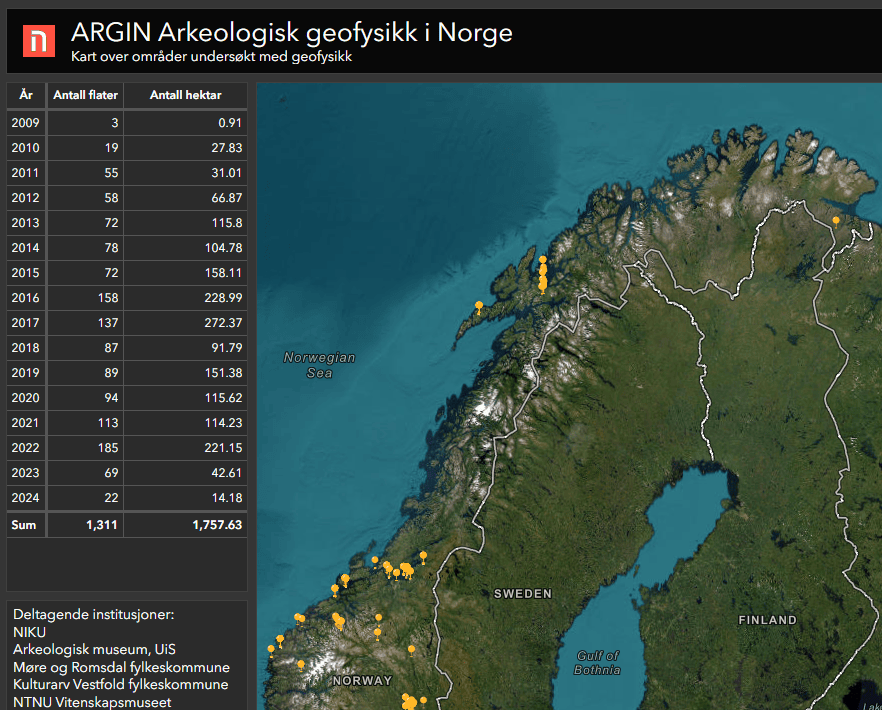
Archaeological Geophysics – launch of map service argin.no
NIKU (with partners) has created an open map service with an overview of projects completed with archaeological geophysics in Norway. Almost 2000 hectares have been studied and 300 project reports are now available through the webpage argin.no.

Linking Places
Save the date for the conference Linking Places in the Emerging Viking Age on the 17. and 18. October 2024! More information to come early next year.
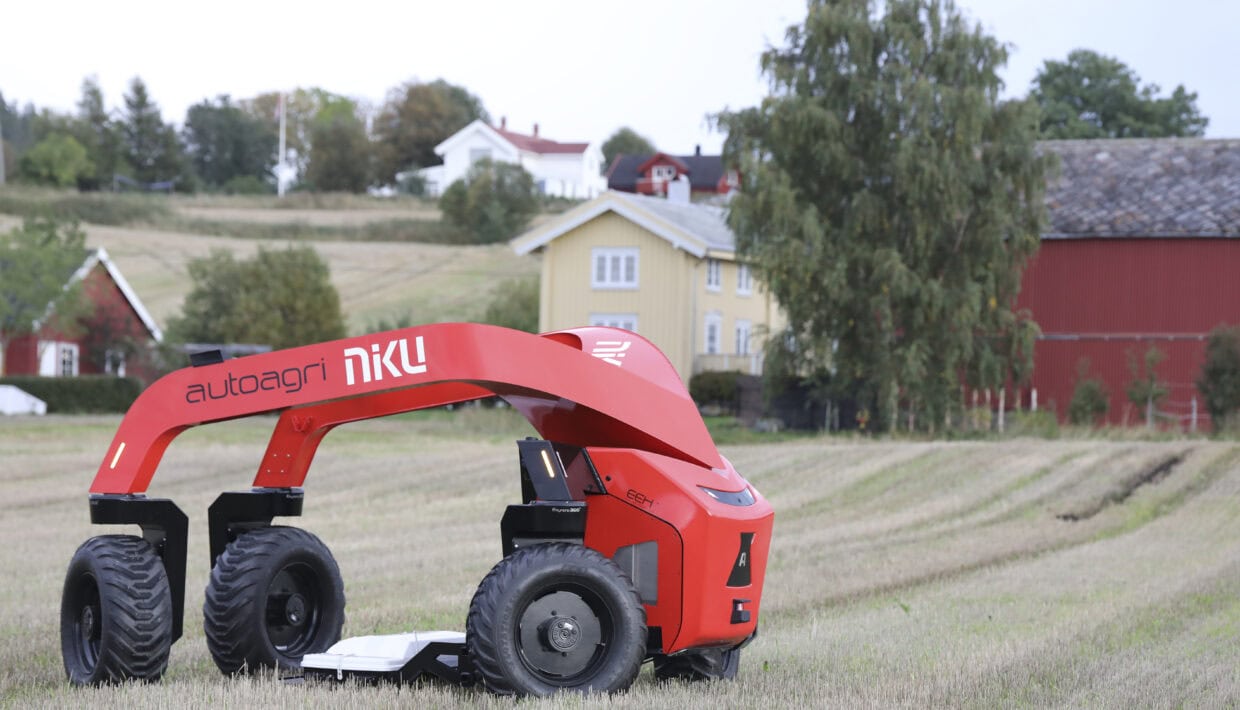

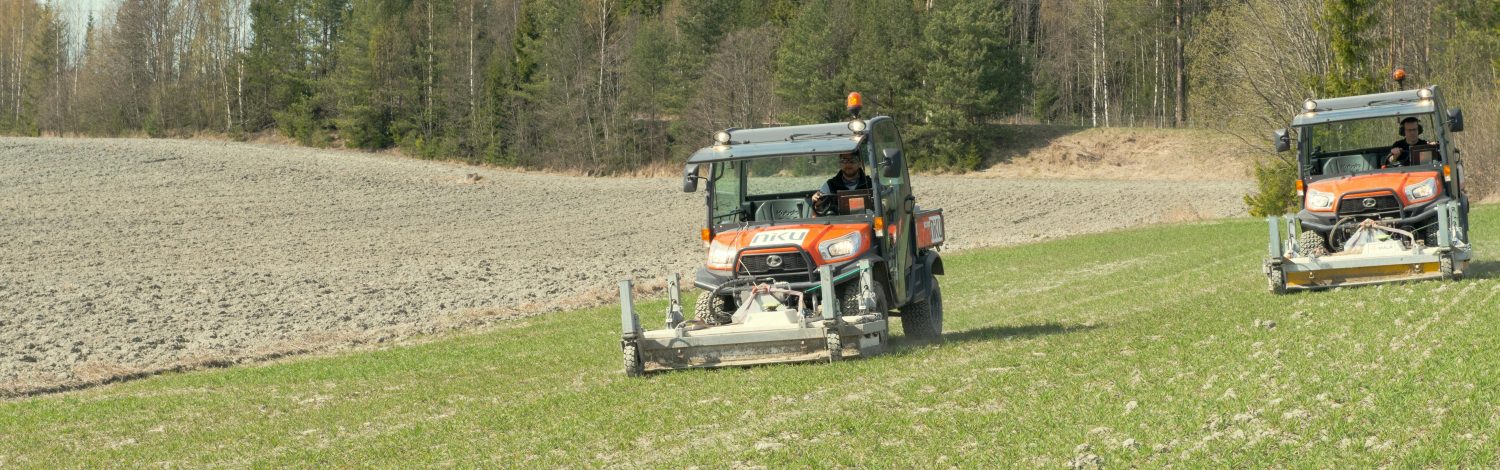
Innovative Technology: Robot to Find Norway’s Hidden Cultural Heritage
The Norwegian Institute for Cultural Heritage Research (NIKU) and AutoAgri are launching a revolutionary self-driving ground penetrating radar (GPR) for archaeological survey. The technology promises increased efficiency, climate friendly solutions, and accurate mapping of hitherto undiscovered cultural heritage.
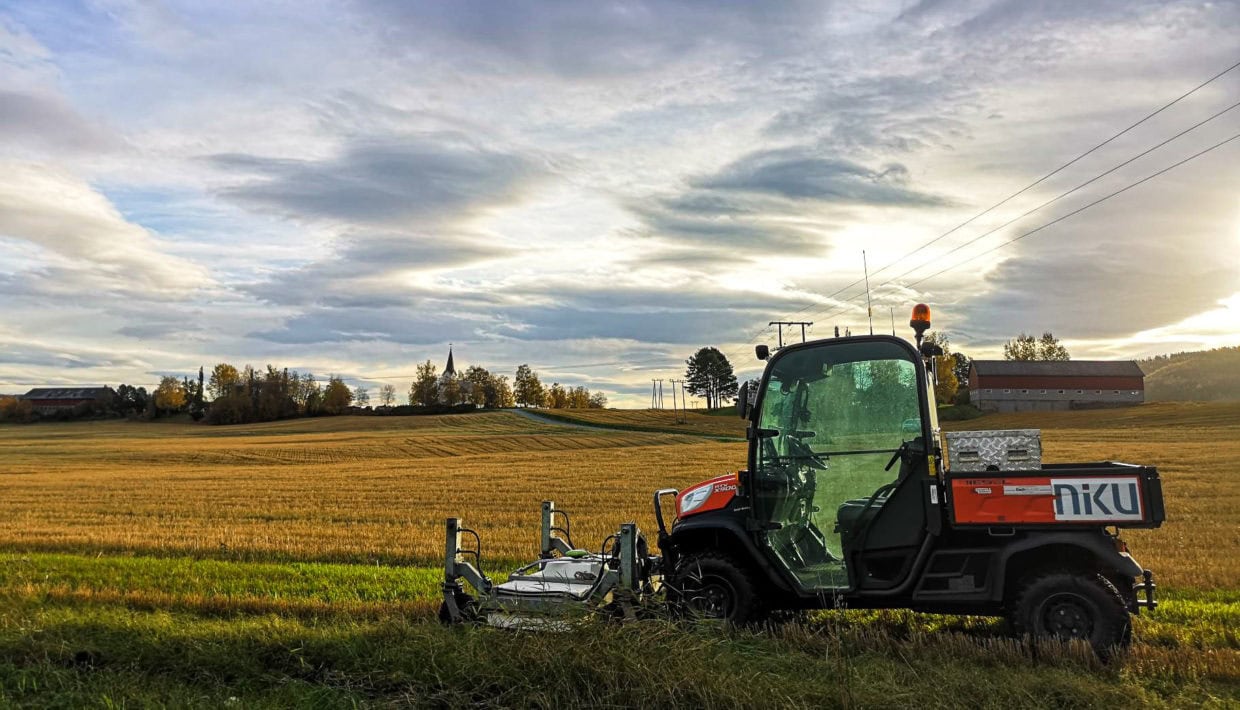

Using GPR to Shed Light on State Formation, National Unification and Religious Change in Norway
Last autumn, archaeologists using ground-penetrating radar (GPR) discovered traces of previously unknown graves and settlement activity at several locations along Trondheim Fjord. They hope that these discoveries can shed light on state formation, national unification and religious change in Norway a thousand years ago.
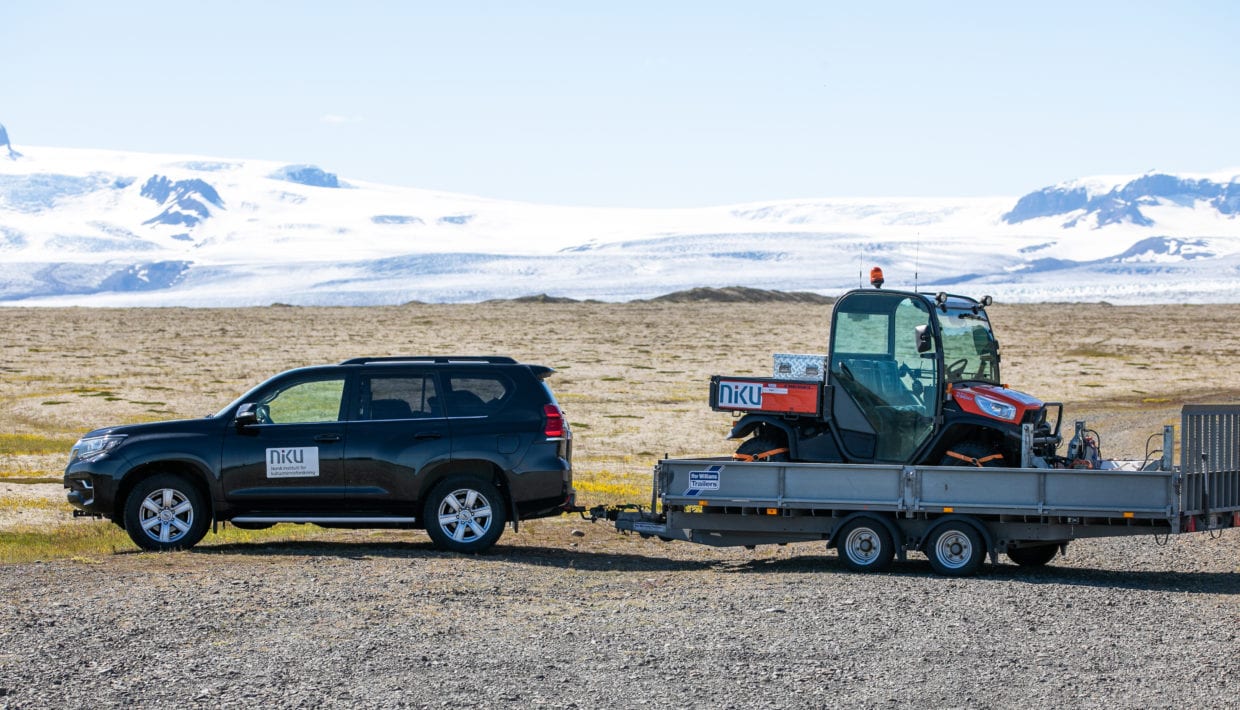

Promising results with ground-penetrating radar in Iceland
This summer, archaeologists from Norwegian Institute for Cultural Heritage (NIKU) have carried out several surveys using ground penetrating radar in Iceland. Preliminary results show that the investigations have already been very successful.
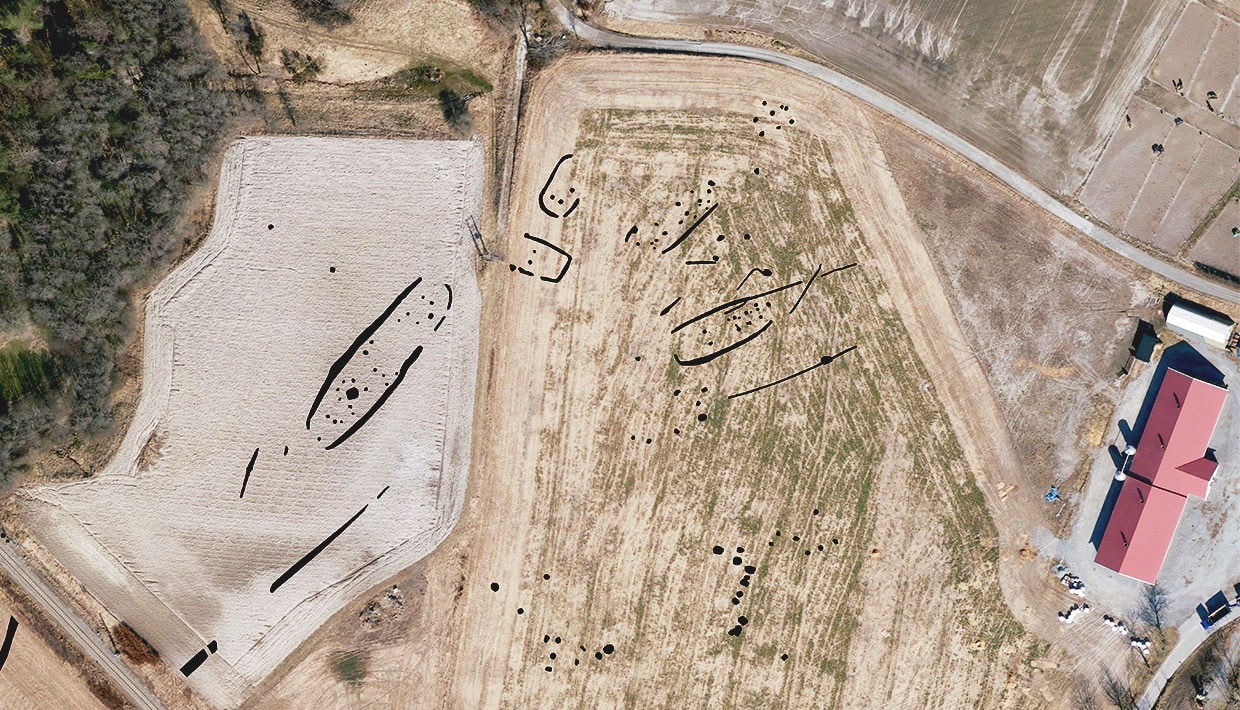

60 metre longhouse discovered with GPR near Viking ship at Gjellestad
At Gjellestad in Norway, archaeologists from the Norwegian Institute for Cultural Heritage Research (NIKU) have found a 60 metre longhouse. There is no longer a doubt that Gjellestad, where the same team discovered a Viking ship in 2018, has been a central place in the late Nordic Iron Age. In the next few years, researchers will hopefully find the answer to how Gjellestad became such an important place.
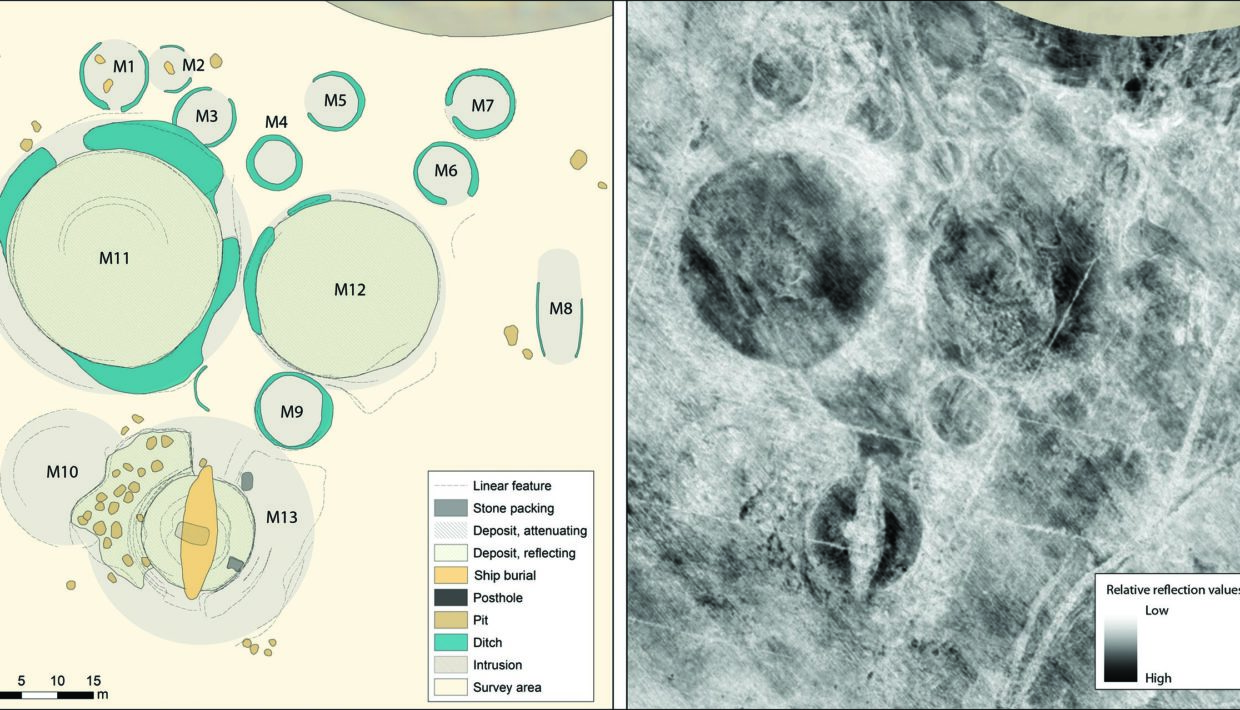
Press release: Viking Ship Burial and Ritual Centre found without digging
Archaeologists in Norway have identified a previously unknown ritual centre, including a feast hall, cult house, and ship burial.
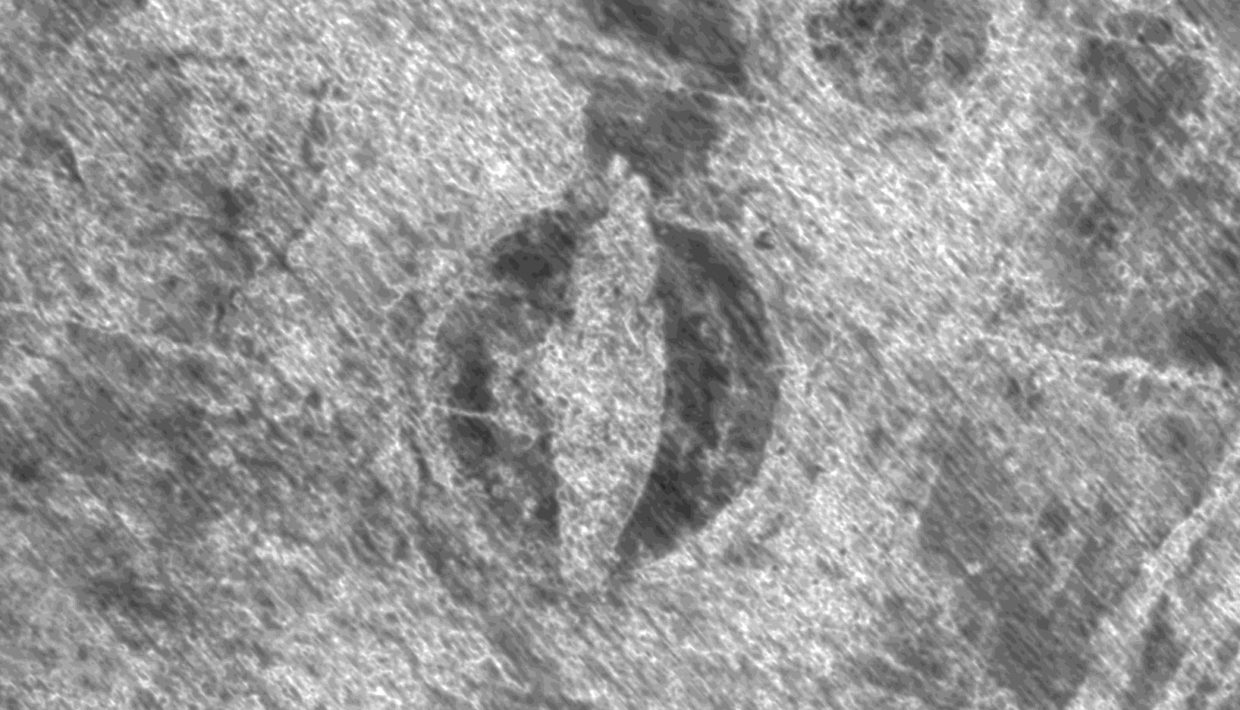

First Viking ship excavation in a 100 years starts now
"This will be exciting for all of us, regardless of whether you are an archaeologist or just have a medium interest in our past," says Viking ship expert Knut Paasche.

The Gjellestad Ship confirmed to be from the Viking Age
The Gjellestad Ship is quite clearly from the Viking Age, the Museum of Cultural History said today. “The investigations happily confirm our hypothesis from 2018, when we found the ship by ground-penetrating radar (GPR),” says Knut Paasche, head of NIKU’s department of digital archaeology.




